Pleura, Pleural Effusions, & Pleural Thickening
The thorax is the part of the body between the head and abdomen; commonly called the chest. The heart and lungs reside in the thoracic cavity (among other things) and are protected by the rib cage and sternum.
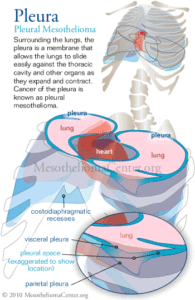
The mesothelial membrane which lines the chest and lungs is known as the pleura. This thin membrane folds over on itself, creating two layers which can then easily slip against one another, allowing the lungs to expand and contract.
Where it touches organs, the membranes is known as the visceral pleura. The "exterior" or outer layer of membrane is called the parietal pleura.
The cells of the pleura produce fluid which resides between the layers, lubricating their movement. This space between the layers is known as the pleural cavity. At the bottom of the pleural cavity is a potential space known as costodiaphragmatic recess; the lungs expand into this area when they take in air.
The thorax is the part of the body between the head and abdomen; commonly called the chest. The heart and lungs reside in the thoracic cavity (among other things) and are protected by the rib cage and sternum.
The mesothelial membrane which lines the chest and lungs is known as the pleura. This thin membrane folds over on itself, creating two layers which can then easily slip against one another, allowing the lungs to expand and contract.
Where it touches organs, the membranes is known as the visceral pleura. The "exterior" or outer layer of membrane is called the parietal pleura.
The cells of the pleura produce fluid which resides between the layers, lubricating their movement. This space between the layers is known as the pleural cavity. At the bottom of the pleural cavity is a potential space known as costodiaphragmatic recess; the lungs expand into this area when they take in air.
If excess fluid builds up between the layers, this is known as a pleural effusion. Pleural effusions may be a build up of serous or pleural fluid, or may be blood, pus, or chyle (sounds like the name "Kyle," chyle is a milky fluid consisting of lymph and emulsified fats). A pleural effusion can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs as they attempt to inhale.
Dyspnea, or shortness of breath, is a common symptom of a pleural effusion. Rapid breathing (tachypnea), coughing, and a blue tinge to the skin (cyanosis) may also by symptoms of a pleural effusion. A pleural effusion may also be asymptomatic (cause no symptoms) and may simply be discovered during a physical exam or seen on an x-ray.
Cancer of the pleura is known as malignant pleural mesothelioma. A novel treatment for pleural mesothelioma is an extrapleural pneumonectomy, where the parietal pleura is removed along with parts of the lung, pericardium (membrane covering the heart), and part of the diaphragm. Heated chemotherapy may be used to "wash" the thoracic cavity.